RMK Merrill-Stevens boat mechanic inspects and repairs
RMK Merrill-Stevens boat mechanic inspects and repairs engines, propellers, steering systems, and other equipment of marine crafts.
He or she also performs rigging work, including installing winches and throttle controls.
Boat dealers, marinas, and watercraft manufacturers employ most marine mechanics. High school diplomas or the equivalent are generally required for entry-level jobs.
Engine
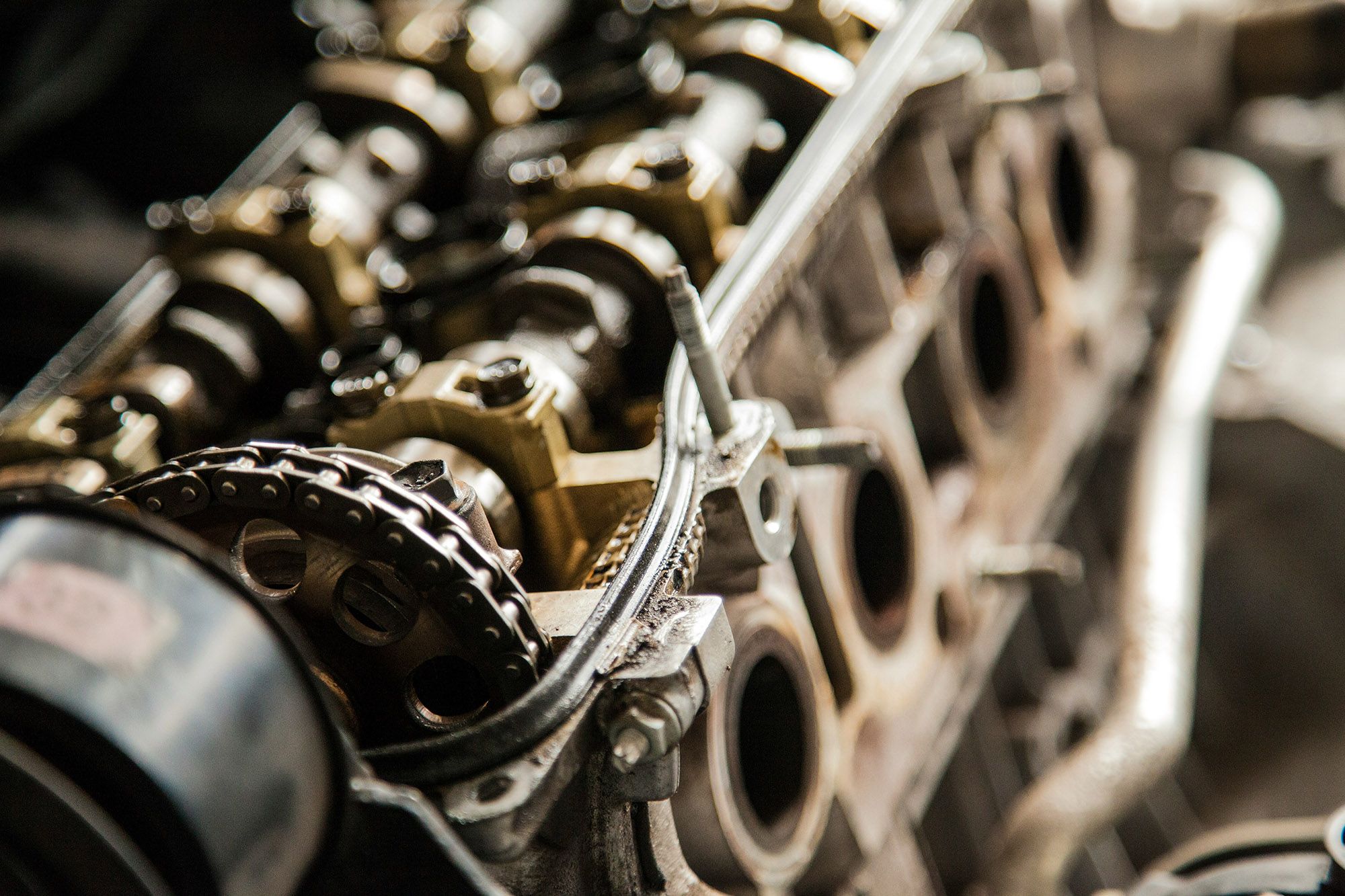
The engine is the heart of a boat, and it's essential to keep yours in tip-top condition. You can do several things to keep your engine running smoothly, from cleaning the air filter to changing the oil.
Taking the time to do these things will help to keep your boat in good condition and increase its lifespan. In addition, they will save you money on fuel.
Before you take your boat out, checking the engine and ensuring that all the major components are working correctly is a good idea. It would be best to lubricate spark plug holes, replace cracked hoses, and change the oil. This is a great way to ensure your engine runs all year round smoothly.
Propeller
Propellers are the primary connection between your engine and the water - they affect every phase of boat performance - handling, riding, comfort, speed, acceleration, engine life, fuel economy, and safety.
A propeller has blades that twist from the hub to the tip (see Figure 4-1), forming an airfoil shape as they move through the water. This reduces the force that needs to be exerted on the blades at the tips compared to the forces at the hub.
Increasing the angle of the blades increases the amount of thrust produced by the propeller. However, this can lead to a higher overall system cost due to the extra blade material needed and increased blade-to-blade interference effects.
Generally, the rake of a propeller should increase for surfacing operations and decrease for non-surfacing operations. A higher rake will also improve a propeller's ability to operate in cavitating or ventilating situations, such as when the blades break the water's surface.
Batteries
Batteries are devices that accept, store, and release electricity. This is done through a chemical reaction that converts chemical potential energy into electrical energy.
A chemical material separates the battery's two electrodes (cathode and anode) called an electrolyte. An external circuit connects the two ends, allowing electrons to move back and forth.
There are many different types of batteries on the market. Generally, the type of chemistry used inside them determines their performance characteristics.
Electrical

Electricity is a form of energy that we use to power everything from light bulbs and televisions to computers. It works by moving electrons out of their orbits, creating magnetic fields that kickstart the formation of an electrical current.
Getting familiar with the basics of electricity can help you troubleshoot any problems on your boat. Whether you’re a professional marine mechanic or an occasional do-it-yourselfer, understanding how the electrical system works can save you a lot of headaches down the road.
Ideally, an excellent marine electrician will inspect your boat’s electrical system twice a year. This way, they’ll know what to look for and catch problems early on before they become significant issues.
Fuel

Fuels are liquid substances that can be used to generate energy, and they can also be used to lubricate and cool engine parts and prevent the formation of deposits.
Modern gasoline has been refined to promote low automobile emissions, and it’s commonly mixed with ethanol. Ethanol is hygroscopic, which means it absorbs water. When enough ethanol-water mixture sinks to the bottom of the tank, it creates a corrosive slurry that can damage your boat’s engine.
Marine engines are designed to run on fuel with no more than 10% ethanol, the maximum ethanol content allowed by boat manufacturers. Higher ethanol levels in your boat’s fuel can corrode and dry out rubber components, clog filters, and cause internal corrosion.
Similar Blogs

Copyright © 2024 RMK MERRILL STEVENS, All rights reserved.





